Create an S3 Bucket for File Uploads
Now that we have our database table ready; let’s get things set up for handling file uploads. We need to handle file uploads because each note can have an uploaded file as an attachment.
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) provides storage service through web services interfaces like REST. You can store any object in S3 including images, videos, files, etc. Objects are organized into buckets, and identified within each bucket by a unique, user-assigned key.
In this chapter, we are going to create an S3 bucket which will be used to store user uploaded files from our notes app.
Create Bucket
First, log in to your AWS Console and select S3 from the list of services.
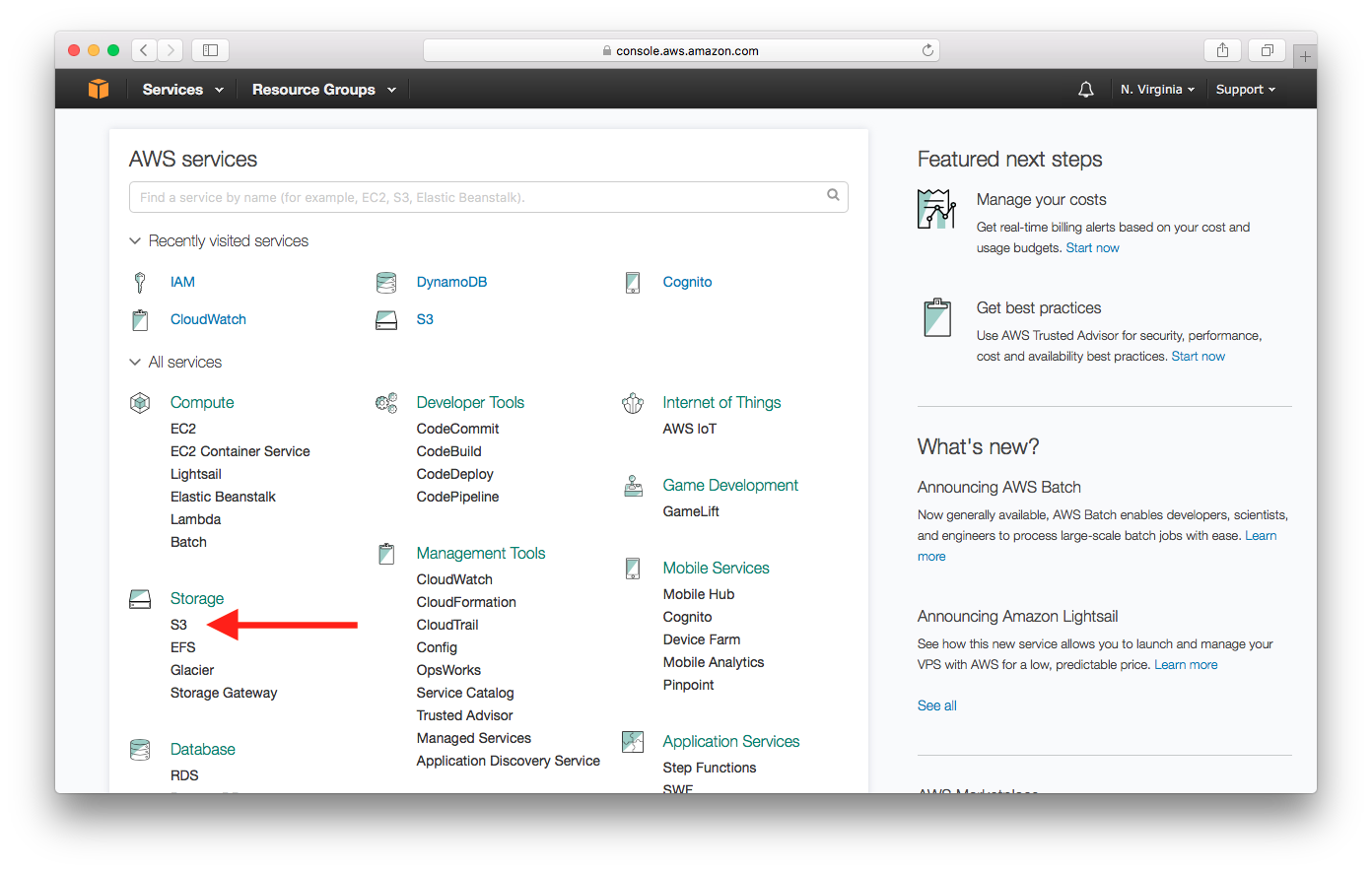
Select Create bucket.
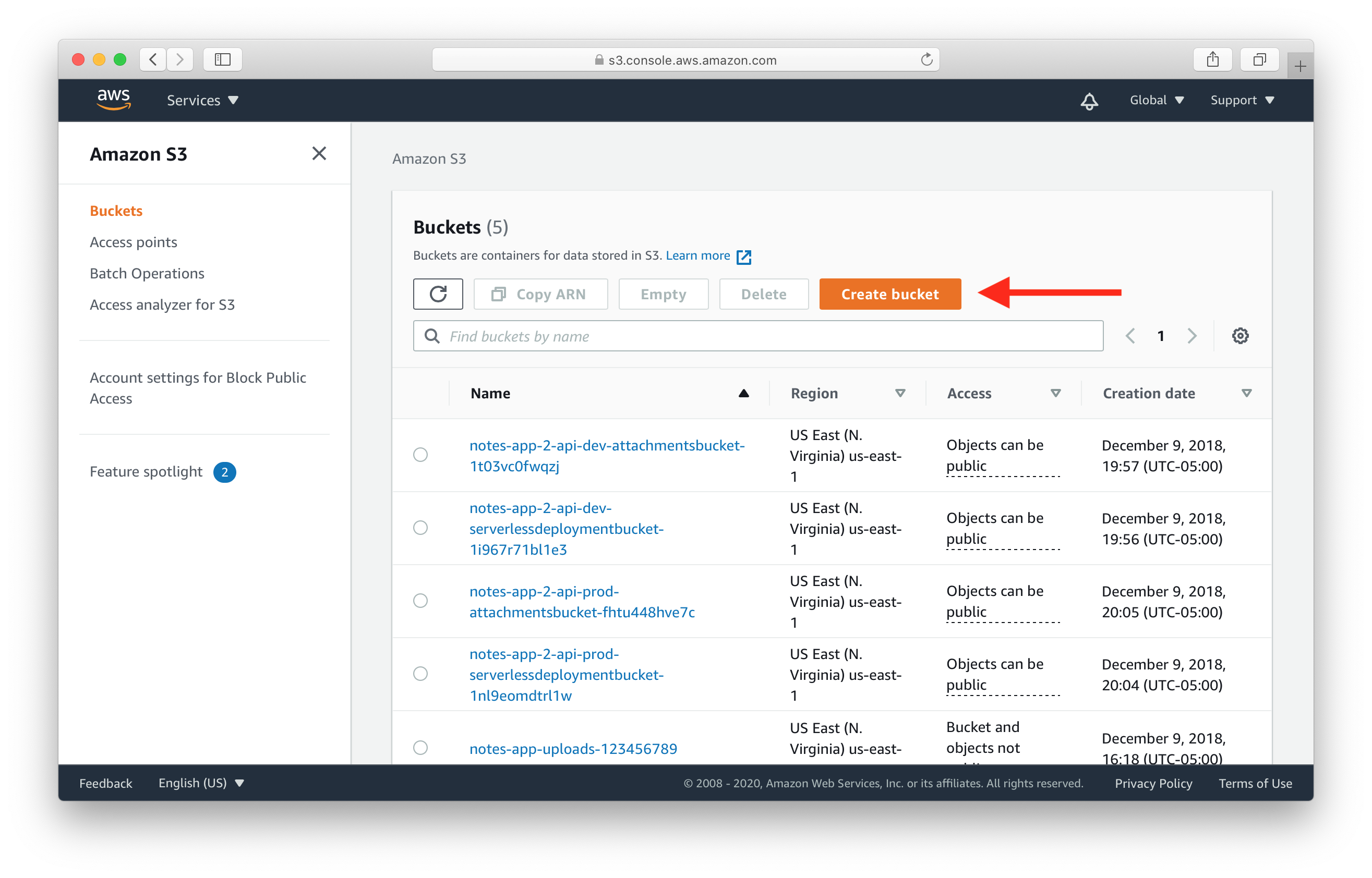
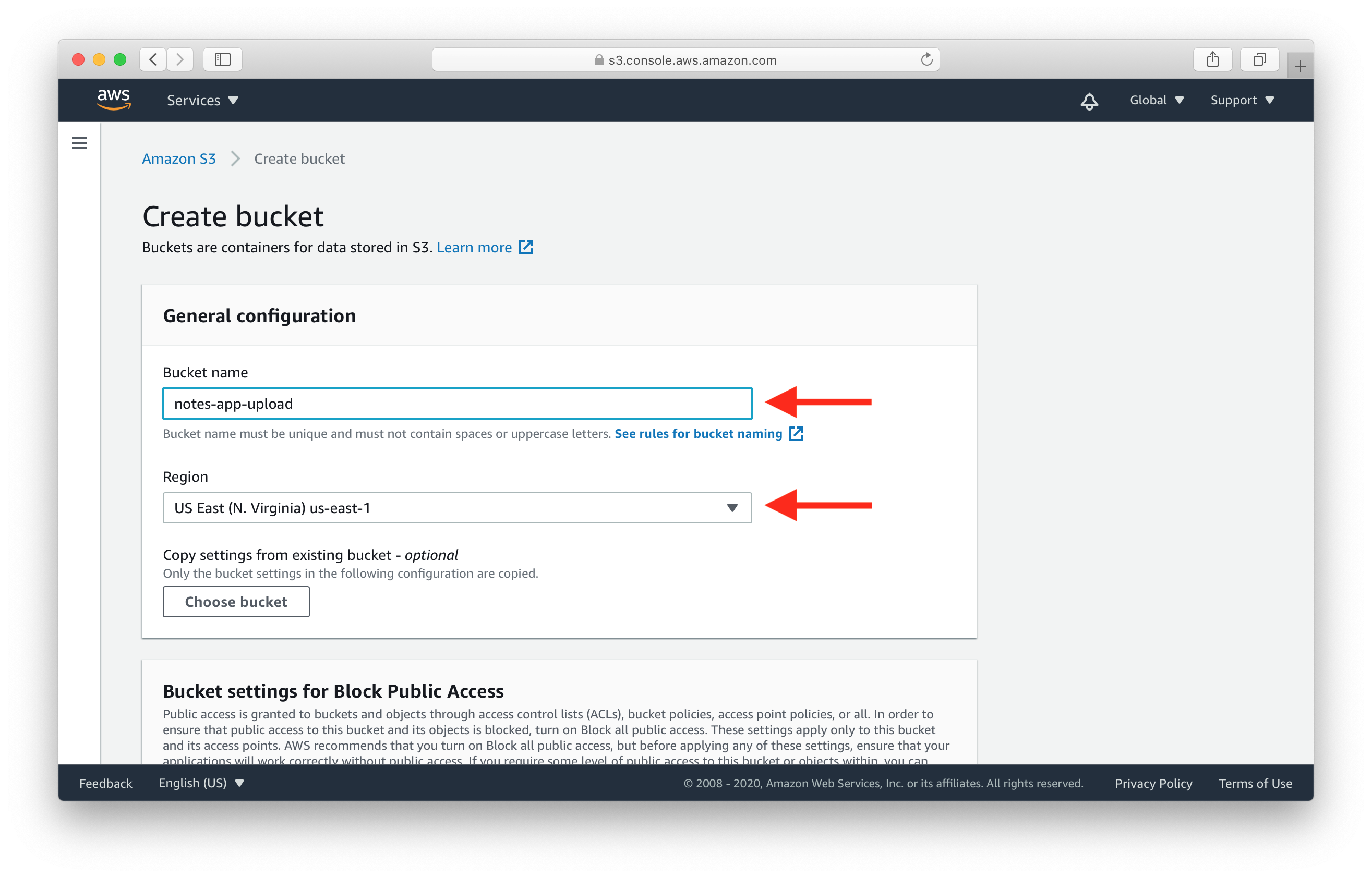
Pick a name of the bucket and select a region. Then select Create.
- Bucket names are globally unique, which means you cannot pick the same name as this tutorial.
- Region is the physical geographical region where the files are stored. We will use US East (N. Virginia) for this guide.
Make a note of the name and region as we’ll be using it later in the guide.
Then scroll all the way down and click Create bucket.
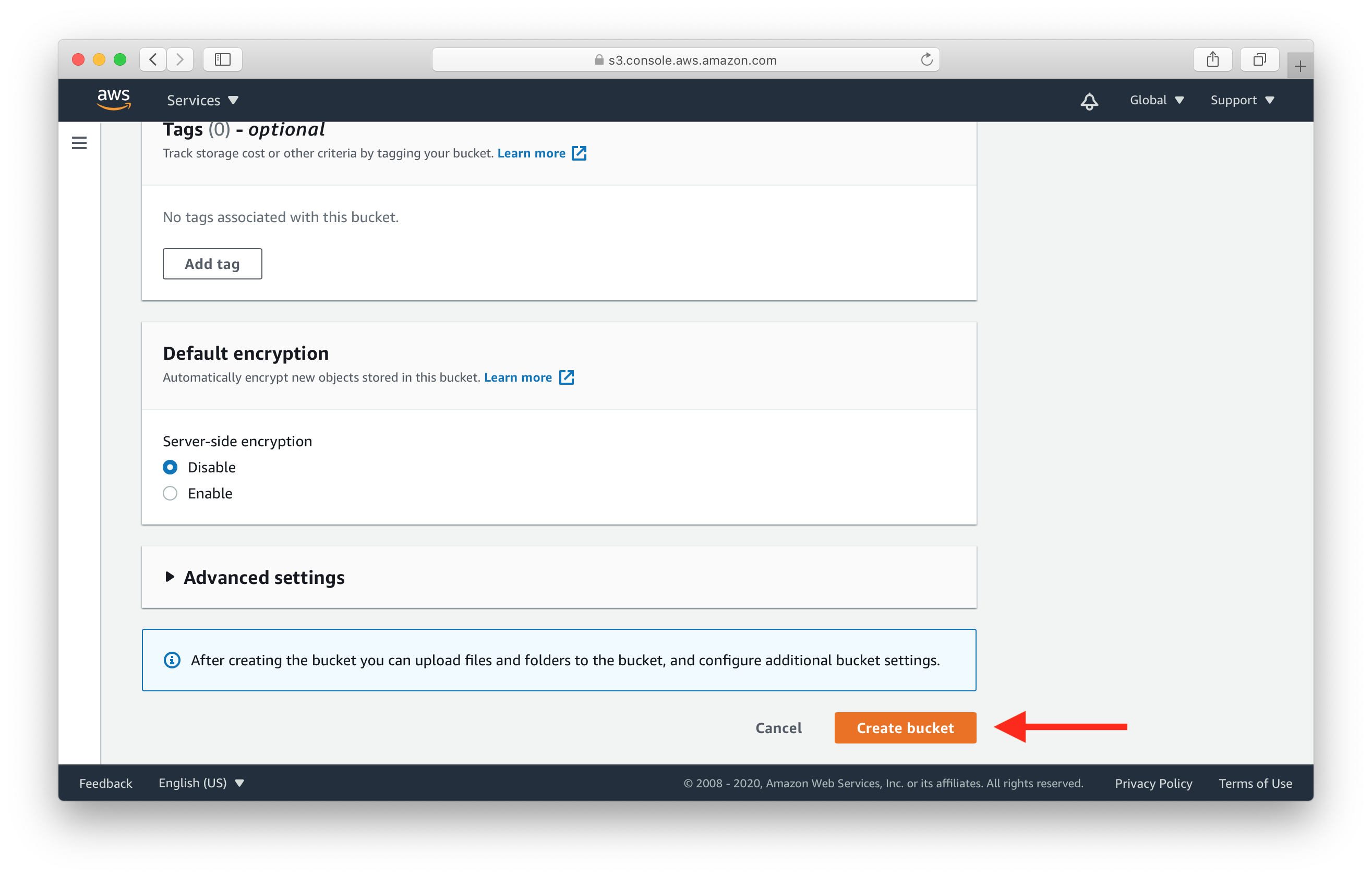
This should create your new S3 bucket. Before we move on, we need to make sure that our React.js frontend will be able to upload files to this bucket. Since it’ll be hosted on a different domain, we need to enable CORS.
Select the newly created bucket from the list.
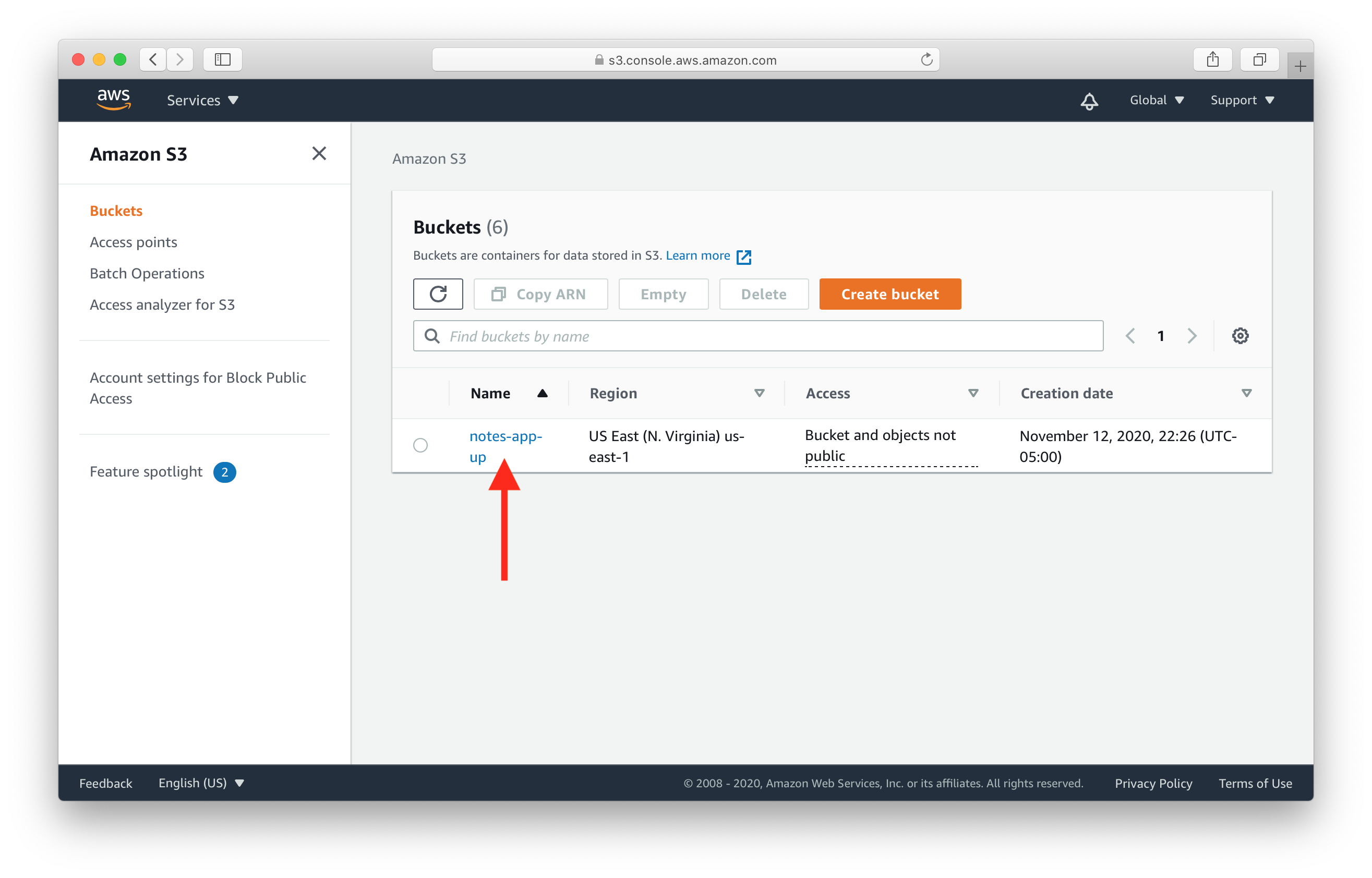
Select the Permissions tab
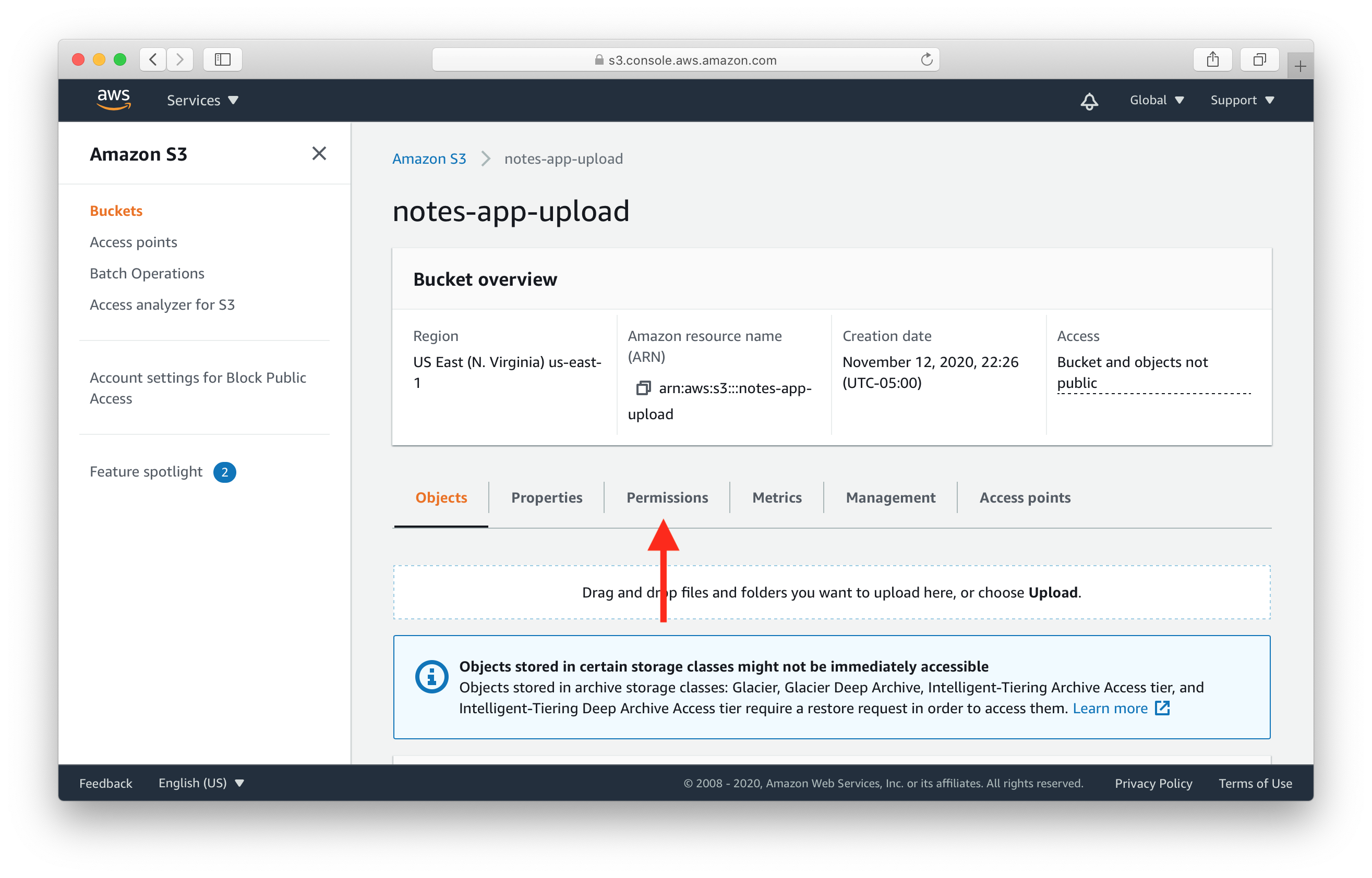
Then scroll down to the Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) section and hit Edit.
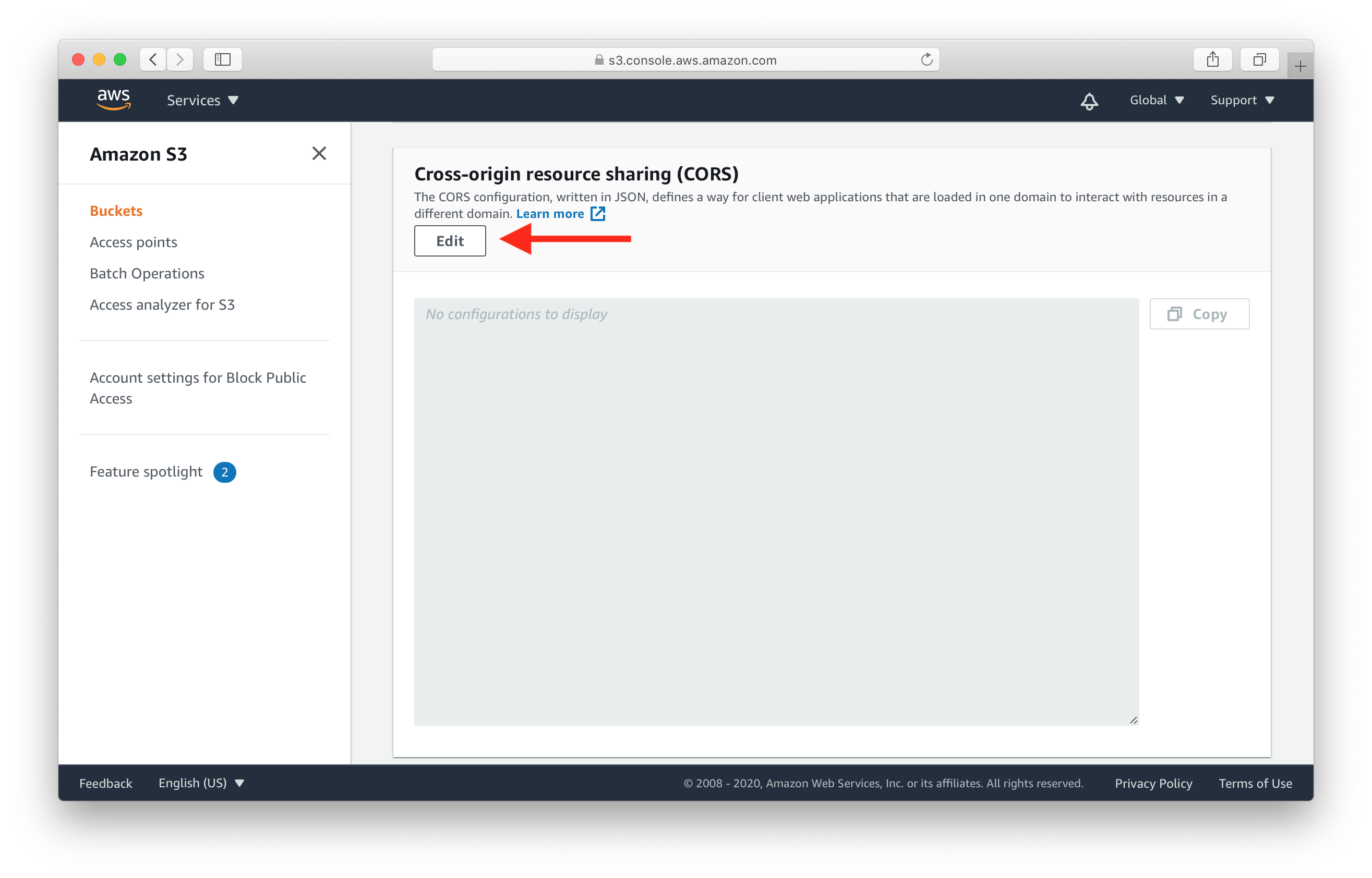
Paste the following CORS configuration into the editor, then hit Save changes.
[
{
"AllowedHeaders": [
"*"
],
"AllowedMethods": [
"GET",
"PUT",
"POST",
"HEAD",
"DELETE"
],
"AllowedOrigins": [
"*"
],
"ExposeHeaders": [],
"MaxAgeSeconds": 3000
}
]
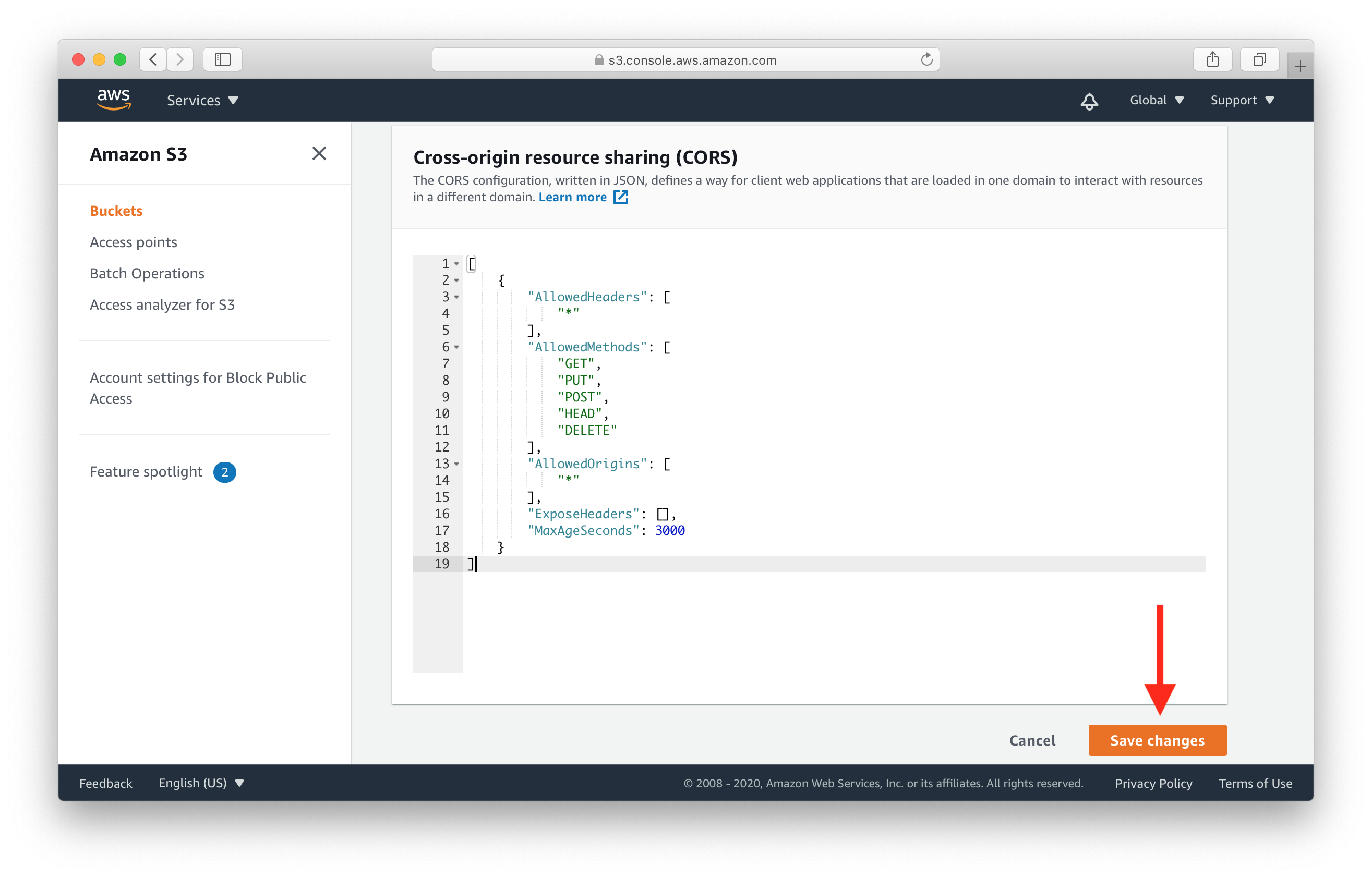
Note that, you can customize this configuration to use your own domain or a list of domains when you use this in production.
Next we are going to start working on our serverless API backend.
For help and discussion
Comments on this chapter