How to use Middy to validate your serverless API requests
In this example we will look at how to use the Middy validator middleware with a serverless API to validate request and response schemas.
Requirements
- Node.js 16 or later
- We’ll be using TypeScript
- An AWS account with the AWS CLI configured locally
What is Middy
Middy is a very simple middleware engine that allows you to simplify your AWS Lambda code when using Node.js. It allows you to focus on the strict business logic of your Lambda function and then attach additional common elements like authentication, authorization, validation, serialization, etc. in a modular and reusable way by decorating the main business logic.
Create an SST app
 Let’s start by creating an SST app.
Let’s start by creating an SST app.
$ npx create-sst@latest --template=base/example middy-validator
$ cd middy-validator
$ npm install
By default, our app will be deployed to the us-east-1 AWS region. This can be changed in the sst.config.ts in your project root.
import { SSTConfig } from "sst";
export default {
config(_input) {
return {
name: "middy-validator",
region: "us-east-1",
};
},
} satisfies SSTConfig;
Project layout
An SST app is made up of a couple of parts.
-
stacks/— App InfrastructureThe code that describes the infrastructure of your serverless app is placed in the
stacks/directory of your project. SST uses AWS CDK, to create the infrastructure. -
packages/functions/— App CodeThe code that’s run when your API is invoked is placed in the
packages/functions/directory of your project.
Create our infrastructure
Our app is made up of a simple API. The API will read two variables from the request and return a greeting message as a response.
Creating our API
Let’s start by adding the API.
 Replace the
Replace the stacks/ExampleStack.ts with the following.
import { Api, StackContext } from "sst/constructs";
export function ExampleStack({ stack }: StackContext) {
// Create a HTTP API
const api = new Api(stack, "Api", {
routes: {
"POST /": "packages/functions/src/lambda.handler",
},
});
// Show the endpoint in the output
stack.addOutputs({
ApiEndpoint: api.url,
});
}
We are using the SST Api construct to create our API. It simply has one endpoint (the root). When we make a POST request to this endpoint the Lambda function called handler in packages/functions/src/lambda.ts will get invoked.
 Replace the code in
Replace the code in packages/functions/src/lambda.ts with:
import { APIGatewayProxyHandlerV2 } from "aws-lambda";
export const handler: APIGatewayProxyHandlerV2 = async (event) => {
const { fname, lname } = JSON.parse(event.body);
return {
statusCode: 200,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" },
body: `Hello, ${fname}-${lname}.`,
};
};
We are reading two variables fname and lname from the event body and returning a simple greeting message.
Let’s test what we have so far.
Starting your dev environment
 SST features a Live Lambda Development environment that allows you to work on your serverless apps live.
SST features a Live Lambda Development environment that allows you to work on your serverless apps live.
$ npm run dev
The first time you run this command it’ll take a couple of minutes to deploy your app and a debug stack to power the Live Lambda Development environment.
===============
Deploying app
===============
Preparing your SST app
Transpiling source
Linting source
Deploying stacks
dev-middy-validator-ExampleStack: deploying...
✅ dev-middy-validator-ExampleStack
Stack dev-middy-validator-ExampleStack
Status: deployed
Outputs:
ApiEndpoint: https://bqoc5prkna.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
The ApiEndpoint is the API we just created.
Let’s test our endpoint using the integrated SST Console. The SST Console is a web based dashboard to manage your SST apps Learn more about it in our docs.
Go to the API explorer and click on the POST / route. In the Headers tab set the content-type as JSON Content-type: application/json.
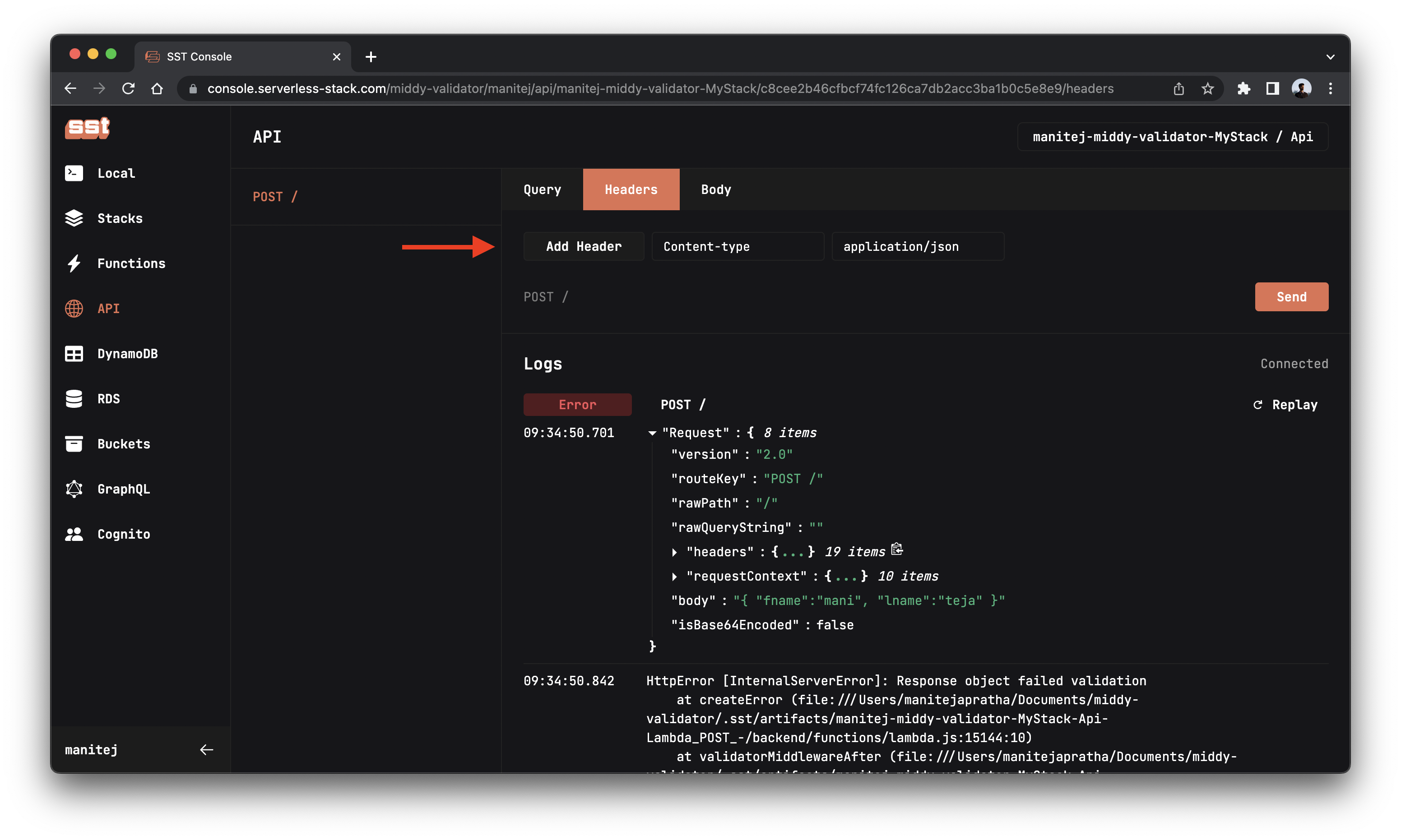
In the Body tab, enter the below JSON and click Send to send a POST request.
{
"fname": "mani",
"lname": "teja"
}
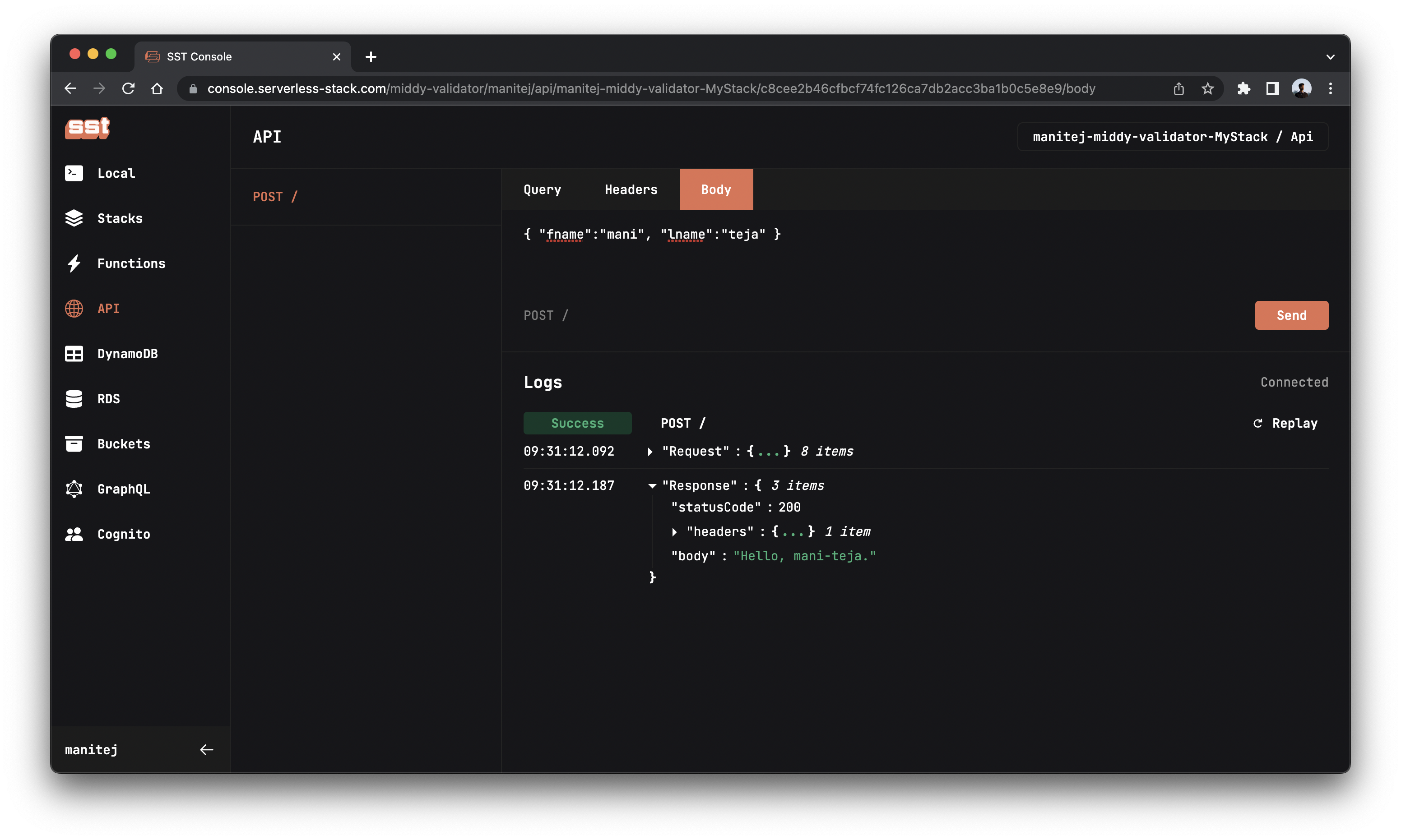
As you can see the endpoint is working as expected. We sent mani and teja as our fname and lname respectively and got Hello, mani-teja as the response.
Now let’s remove lname from the body and see what happens.
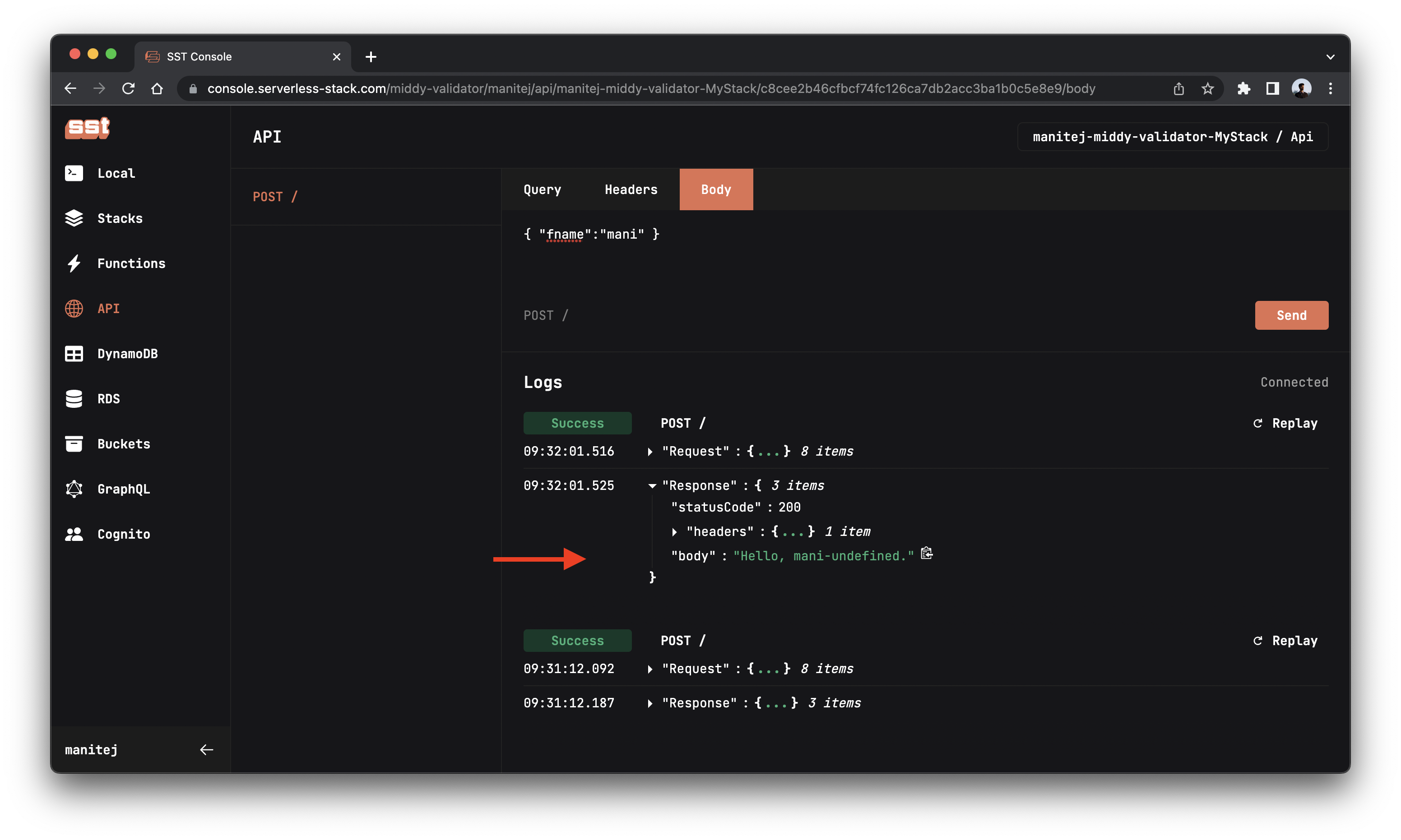
You’ll notice that the endpoint is working fine but it returned undefined for lname. Since we’d only sent the fname in the request, so it returned undefined in the place of lname.
In a production app it can be difficult to catch these issues. We’d like to explicitly throw an error when there is a missing parameter in the request body.
Setting up our Middy middleware
To fix this let’s use the Middy validator middleware to validate our API.
 Run the following in the
Run the following in the packages/functions/ directory.
$ npm install --save @middy/core @middy/http-json-body-parser @middy/http-error-handler @middy/validator
Let’s understand what the above packages are.
| package | explanation |
|---|---|
@middy/core |
The core package of the Middy framework. |
@middy/http-json-body-parser |
A middleware that parses HTTP requests with a JSON body and converts the body into an object. |
@middy/http-error-handler |
A middleware that handles uncaught errors that contain the properties statusCode (number) and message (string) and creates a proper HTTP response for them (using the message and the status code provided by the error object). |
@middy/validator |
A middleware that validates incoming events and outgoing responses against custom schemas defined with the JSON schema syntax. |
Adding request validation
 Replace
Replace packages/functions/src/lambda.ts with the following.
import middy from "@middy/core";
import validator from "@middy/validator";
import httpErrorHandler from "@middy/http-error-handler";
import jsonBodyParser from "@middy/http-json-body-parser";
const baseHandler = (event) => {
// You don't need JSON.parse since we are using the jsonBodyParser middleware
const { fname, lname } = event.body;
return {
statusCode: 200,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" },
body: `Hello, ${fname}-${lname}.`,
};
};
const inputSchema = {
type: "object",
properties: {
body: {
type: "object",
properties: {
fname: { type: "string" },
lname: { type: "string" },
},
required: ["fname", "lname"],
},
},
};
const handler = middy(baseHandler)
.use(jsonBodyParser())
.use(
validator({
inputSchema,
})
)
.use(httpErrorHandler());
export { handler };
Here we are creating an inputSchema. We are explicitly setting that fname and lname are required.
Important: Compiling schemas on the fly will cause a 50-100ms performance hit during cold start for simple JSON Schemas. Precompiling is highly recommended. Read more about this.
Now go back to console and click the Send button again to send a new request.
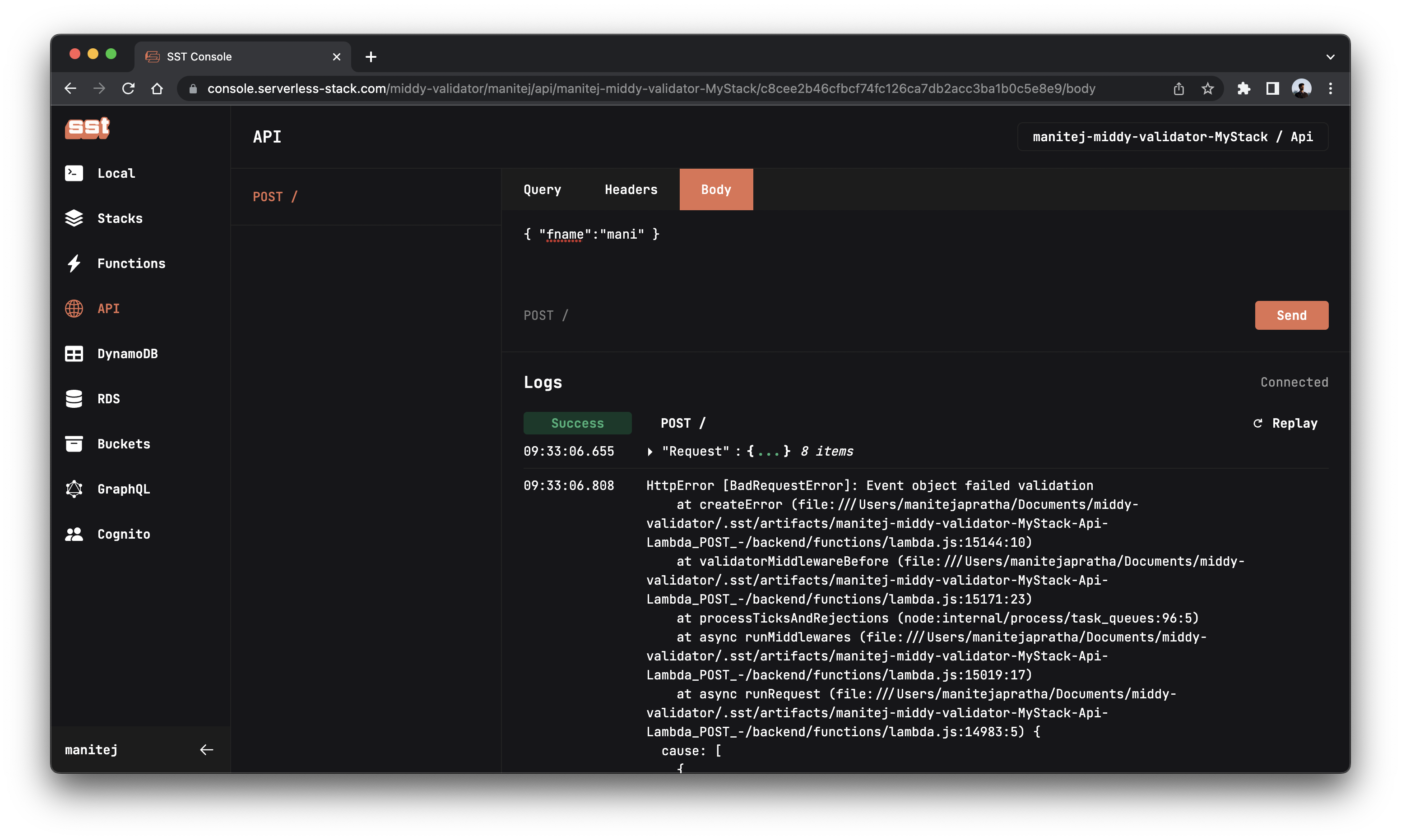
Great! The server throws a Bad request error to let us know that something is wrong.
Adding response validation
While we are here, let’s add response validation as well.
 Replace
Replace packages/functions/src/lambda.ts with this:
import middy from "@middy/core";
import validator from "@middy/validator";
import httpErrorHandler from "@middy/http-error-handler";
import jsonBodyParser from "@middy/http-json-body-parser";
const baseHandler = (event) => {
const { fname, lname } = event.body;
return {
statusCode: 200,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" },
body: `Hello, ${fname}-${lname}.`,
};
};
const inputSchema = {
type: "object",
properties: {
body: {
type: "object",
properties: {
fname: { type: "string" },
lname: { type: "string" },
},
required: ["fname", "lname"],
},
},
};
const outputSchema = {
type: "object",
required: ["body", "statusCode"],
properties: {
body: {
type: "string",
},
statusCode: {
type: "number",
},
headers: {
type: "object",
},
},
};
const handler = middy(baseHandler)
.use(jsonBodyParser())
.use(
validator({
inputSchema,
outputSchema,
})
)
.use(httpErrorHandler());
export { handler };
We added a new outputSchema and added it to the Middy validator.
Let’s test our API again with correct schema and Middy validator.
Add lname parameter again in the Body tab and click Send.

Now the API is back working as expected.
If the schema violates the schema we set in our middleware, the API will throw an error. Let’s quickly try out the case of returning an invalid response.
Instead of returning a number for status code, we’ll return a string instead.
 Replace this line:
Replace this line:
statusCode: 200,
With this:
statusCode: "success",
Let’s test the API again.
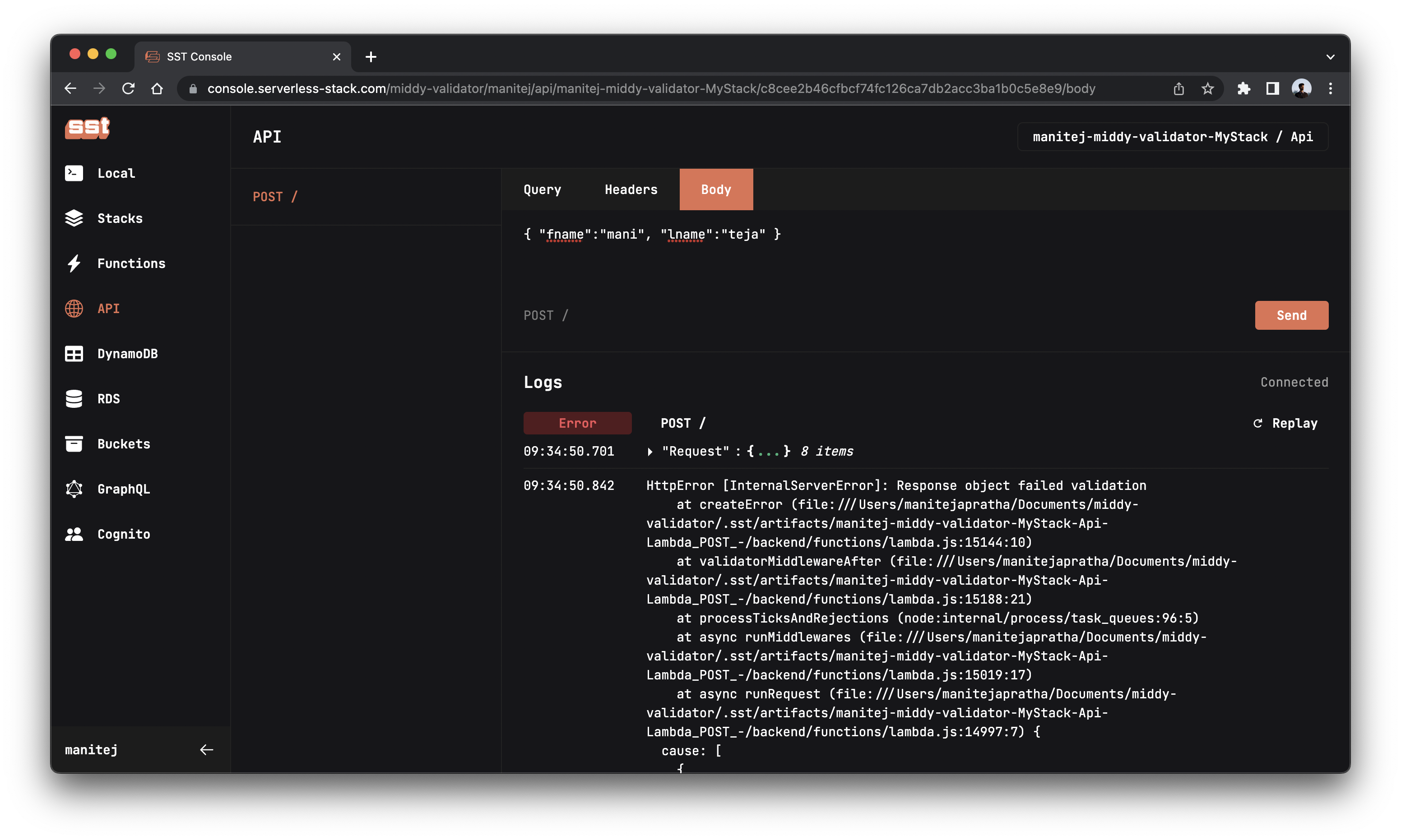
Great! The server now throws a 500 Internal Server Error to let us know that something is wrong.
 Let’s change the status code back.
Let’s change the status code back.
statusCode: 200,
Deploying to prod
 To wrap things up we’ll deploy our app to prod.
To wrap things up we’ll deploy our app to prod.
$ npx sst deploy --stage prod
This allows us to separate our environments, so when we are working in dev, it doesn’t break the app for our users.
Once deployed, you should see something like this.
✅ prod-middy-validator-ExampleStack
Stack prod-middy-validator-ExampleStack
Status: deployed
Outputs:
ApiEndpoint: https://bqoc5prkna.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
Cleaning up
Finally, you can remove the resources created in this example using the following commands.
$ npx sst remove
$ npx sst remove --stage prod
Conclusion
And that’s it! We’ve got a completely validated serverless API. A local development environment, to test and make changes. And it’s deployed to production as well, so you can share it with your users. Check out the repo below for the code we used in this example. And leave a comment if you have any questions!
Example repo for reference
github.com/sst/sst/tree/master/examples/middy-validatorFor help and discussion
Comments on this exampleMore Examples
APIs
-
REST API
Building a simple REST API.
-
WebSocket API
Building a simple WebSocket API.
-
Go REST API
Building a REST API with Golang.
-
Custom Domains
Using a custom domain in an API.
Web Apps
-
React.js
Full-stack React app with a serverless API.
-
Next.js
Full-stack Next.js app with DynamoDB.
-
Vue.js
Full-stack Vue.js app with a serverless API.
-
Svelte
Full-stack SvelteKit app with a serverless API.
-
Gatsby
Full-stack Gatsby app with a serverless API.
-
Angular
Full-stack Angular app with a serverless API.
Mobile Apps
GraphQL
Databases
-
DynamoDB
Using DynamoDB in a serverless API.
-
MongoDB Atlas
Using MongoDB Atlas in a serverless API.
-
PostgreSQL
Using PostgreSQL and Aurora in a serverless API.
-
CRUD DynamoDB
Building a CRUD API with DynamoDB.
-
PlanetScale
Using PlanetScale in a serverless API.
Authentication
Using SST Auth
-
Facebook Auth
Adding Facebook auth to a full-stack serverless app.
-
Google Auth
Adding Google auth to a full-stack serverless app.
Using Cognito Identity Pools
-
Cognito IAM
Authenticating with Cognito User Pool and Identity Pool.
-
Facebook Auth
Authenticating a serverless API with Facebook.
-
Twitter Auth
Authenticating a serverless API with Twitter.
-
Auth0 IAM
Authenticating a serverless API with Auth0.
Using Cognito User Pools
-
Cognito JWT
Adding JWT authentication with Cognito.
-
Auth0 JWT
Adding JWT authentication with Auth0.
-
Google Auth
Authenticating a full-stack serverless app with Google.
-
GitHub Auth
Authenticating a full-stack serverless app with GitHub.
-
Facebook Auth
Authenticating a full-stack serverless app with Facebook.
Async Tasks
-
Cron
A simple serverless Cron job.
-
Queues
A simple queue system with SQS.
-
Pub/Sub
A simple pub/sub system with SNS.
-
Resize Images
Automatically resize images uploaded to S3.
-
Kinesis data streams
A simple Kinesis Data Stream system.
-
EventBus
A simple EventBridge system with EventBus.
Editors
-
Debug With VS Code
Using VS Code to debug serverless apps.
-
Debug With WebStorm
Using WebStorm to debug serverless apps.
-
Debug With IntelliJ
Using IntelliJ IDEA to debug serverless apps.
Monitoring
Miscellaneous
-
Lambda Layers
Using the @sparticuz/chromium layer to take screenshots.